MSME Sector (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises) in India is one of the largest contributor to National GDP of India. MSME Stands for Micro Small and Medium Enterprises.
Micro Small and Medium Enterprises
MSME (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises) definitions have been revised with additional criterion of turnover and upward revision of investment limits. Further, distinction between manufacturing and service sector has been eliminated. The revised definition will not include exports in the overall turnover for MSME classification.
Classification of micro small and medium enterprises
The revised criteria for classification as MSME (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises) is given below: classification of micro small and medium enterprises
- Micro Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ₹1 crore, and turnover does not exceed ₹5 crore.
- Small Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ₹10 crore, and turnover does not exceed ₹50 crore
- Medium Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ₹50 crore, and turnover does not exceed ₹250 crore
classification of micro small and medium enterprises. As per MSME Pulse Report – April 2020, credit to MSMEs (credit exposure up to ₹50 crore) stood at ₹17.75 lakh crore as of January 2020.

MSME Sector in India (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises)
The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) have emerged as an engine of the Indian economy growth. They contribute nearly 30% to India’s GDP, 50% to exports and
provide employment opportunities to more than 11.1 crore skilled and semi-skilled people. There are approximately 6.33 crore MSMEs in the country. Role of micro small and medium enterprises in Indian economy
Micro Small and Medium Enterprises- MSMEs are widening their domain across sectors of the economy, producing a diverse range of products and services to meet demands of domestic as well as global markets.
While COVID-19 impacted business activities, a solid response from the Government and the RBI has provided relief to support growth.
The year under review, saw new definition of MSME based on turnover, launch of Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS), moratorium provided, restructuring, stressed MSME scheme and current account opening guidelines.
MSME Sector is the contribution from The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) and contribute nearly 30% to India’s GDP, 50% to exports and provide employment opportunities to more than 11.1 crore skilled and semi-skilled people.
Consequently, credit demand has resumed to pre-COVID levels. Keeping in mind the disruption caused by the second wave of COVID-19, the Government has extended the scope of the ECLGS Scheme till September 2021 with disbursements being allowed till December 2021.
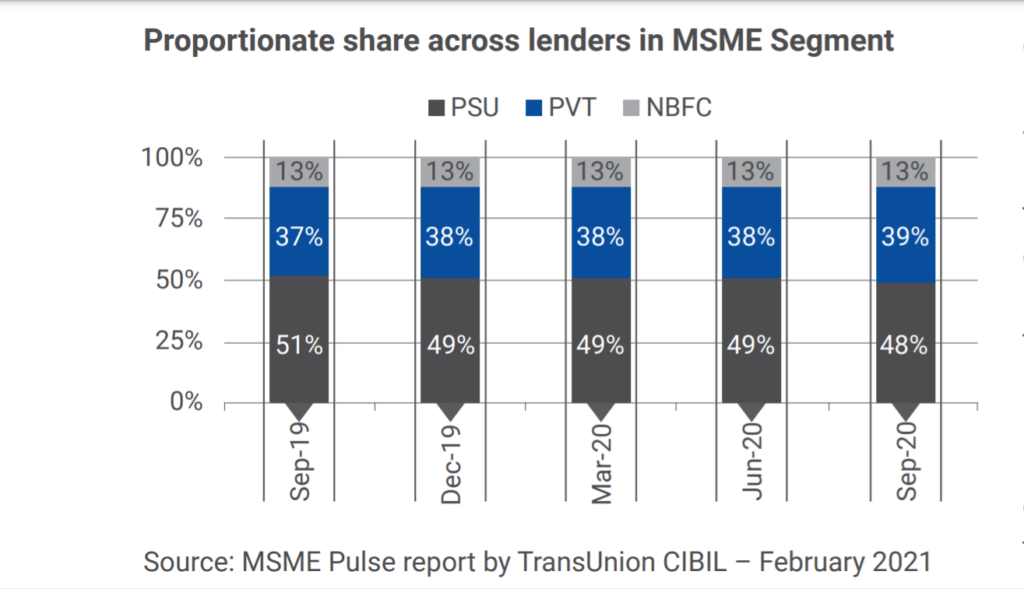
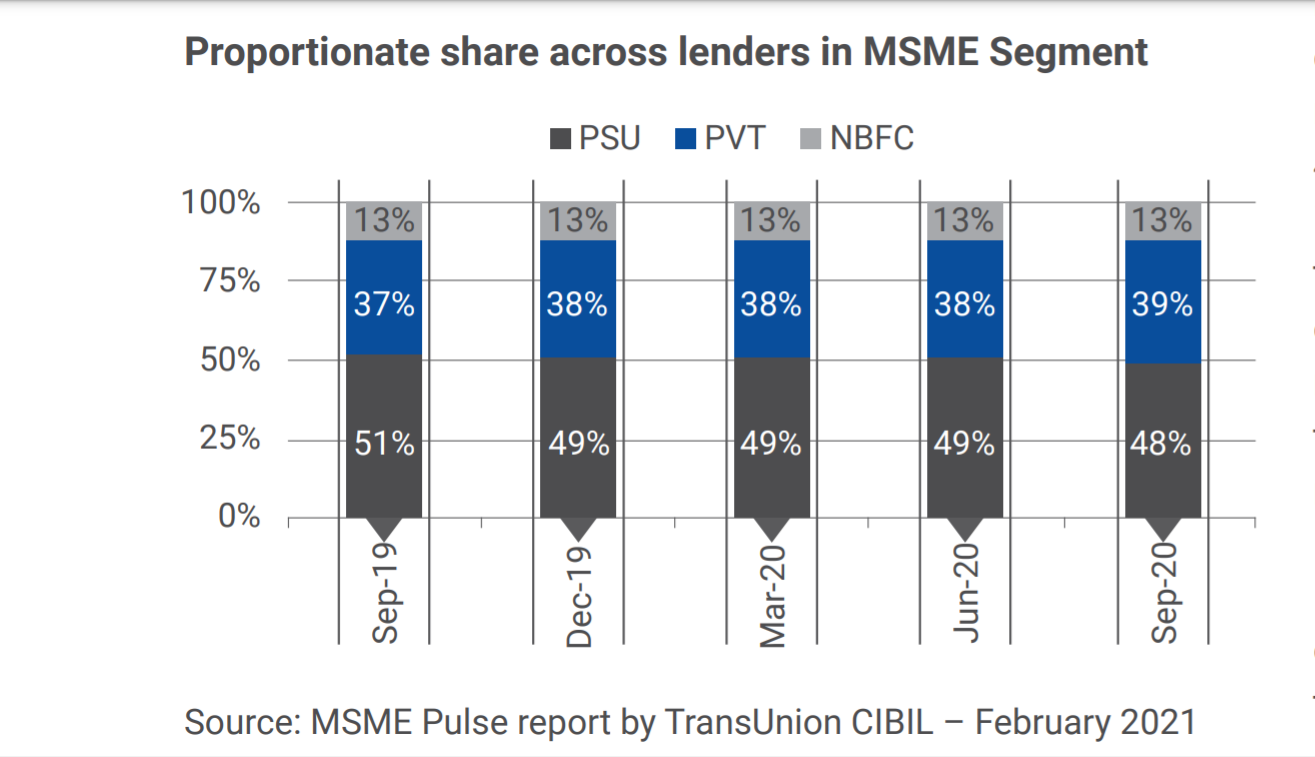
Credit to Micro small and Medium Enterprises
Credit growth to MSMEs (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises) accelerated at a CAGR of 16.3% during FY 2016-17 – FY 2019-20 period. COVID-19 pandemic has brought many behavioural changes in the MSME lending ecosystem. The customer behaviour, customer profile and lenders response to the evolving situation has changed the dynamics of MSME Lending.
Credit infusion to MSMEs declined sharply post the lockdowns due to COVID-19 pandemic. The ECLGS scheme implementation brought the much-needed boost and significantly helped in reviving credit infusion to MSMEs post its announcement in May 2020. The Union Budget has doubled the allocation to MSMEs to ₹15,700 crore for the next financial year 2021-22.
As per the latest MSME Pulse report by TransUnion CIBIL, total on-balance sheet commercial lending in India stood at ₹ 71.25 lakh crore in September 2020. MSME segment’s credit exposure was at ₹ 19.1 lakh crore as of September 2020 registering YoY growth of 5.7% with better trends witnessed in the Micro segment (8-9% YoY), aided by ECLGS disbursements.
Public Sector Banks (PSUs) have taken a lead in MSME (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises) loan originations since April’20 and gained market share. However, recent inquiry trends suggest that Private Banks (PVT) are inching back to pre-COVID levels, with 22% YoY growth in enquiries versus 9% growth for PSUs in December 2020.
Micro Small and Medium Enterprises – MSME Sector in India, challenges of msme sector in India, msme sector means.
Micro Enterprise: turnover does not exceed ₹5 crore.
Small Enterprise: turnover does not exceed ₹50 crore
Medium Enterprise: turnover does not exceed ₹250 crore
Micro Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ₹1 crore, and turnover does not exceed ₹5 crore.
Small Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ₹10 crore, and turnover does not exceed ₹50 crore
Medium Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed ₹50 crore, and turnover does not exceed ₹250 crore